Identifying and supporting vulnerable customers – such as those experiencing financial difficulties, health issues, or emotional distress – is crucial for ethical, compliant and effective service delivery.
While the FCA has long taken a leading role in this space, other regulators such as Ofcom and Ofgem have also required vulnerability protections to be in place, with the UK’s Digital Markets, Competition and Consumers Act 2024 (DMCC), which came into effect on 6 April 2025, also widening the concept of vulnerable customers.
With thresholds higher than ever, the risks of not identifying vulnerable customers can be significant. Fines can now be imposed without a court order and at eye-watering levels, with reputational risk a compounding facto, not to mention the impact on vulnerable individuals themselves.
What’s more, with the divergence between UK and EU law, any cross-border businesses need to be even more on their toes in different jurisdictions.
What is the AI doing to detect vulnerability?
With the preceding three use cases essentially laying the groundwork for this kind of analysis and management, AI can identify signs of vulnerability by analysing speech patterns, language cues, and emotional indicators.
Key benefits: Categorisation and risk scoring
Vulnerability is a spectrum, and customers can move in and out of vulnerable states or between risk factors. Detecting this manually, however, is fraught with difficulty.
First, different people have different – and subjective – views on whether a customer may be indicating a vulnerability factor.
Second, the cues can be subtle and therefore challenging to pick up, especially when an agent – as a normal part of their job – is multi-tasking across multiple screens, taking notes and trying to hold a conversation at the same time.
But the AI is far less likely to miss those cues, because it isn’t distracted, isn’t having a bad or busy day, and doesn’t have empathy as an emotion. Any AI empathy is trained in data, and consequently consistently applied.
Record accuracy
As with use case 1, the use of AI enhances note taking and record-keeping by transcribing and summarising the call automatically. This avoids any temptation to rush the process, and risk non-compliance, while allowing the agent to focus solely on the customer’s needs.
Compliance alerts
While you could employ this kind of analysis in-flight, where prevention is almost always more desirable than cure, even a post-call analysis allows for flagging of potentially vulnerable customers and pro-active outbound or other management of that customer. retrospectively, and still gain some of the benefit, the nature of the regulatory and legal environment makes a real-time approach more desirable, with a prevention rather than cure approach.
Real-time vulnerability detection
The ultimate deployment of real-time detection during a call allows agents to adjust their approach on the fly. And for a true ‘belt and braces’ approach, if a risk score is exceeded, this can be flagged as a ‘red alert’ to the agent, very clearly instructing them not to sell, to do a welfare check, or provide relevant support information.
All of which not only manages the risk to individuals and the business, but empowers agents with the confidence to handle sensitive situations effectively and retains consumer trust through a commitment to their wellbeing that can also foster loyalty.
Implementation Considerations
Again, systems integration and data privacy are key factors in implementation, especially around matters of data usage and consent. As is training and embedding belief in the AI.
But where in other use cases it may be that the cost (or perceived cost) and complexity (or perceived complexity) of implementation of the AI project make the decision more difficult, in this instance, the potential of the AI is less about an ROI against cost than it is about ROI against the potential cost of those eye-watering fines if getting it wrong.
Measuring Success
Here, measurement may be a little trickier, depending upon how well you are able to understand the current baseline. Consider that manual QA is based on only 1-2% of calls, there could be whole swathes of risk going undetected.
The ideal situation is that there is nothing to measure. No issues, no incidents.
However, you can look at measures such as customer feedback from vulnerable customers, the numbers of interventions such as welfare or information provided, and adherence to regulations, particularly if using retrospectively rather than real time.
But the real benefits come from what doesn’t happen, rather than what does. In summary, they are:
- More frequent and consistent identification of customer vulnerability
- More accurate records
- More confidence in your compliance
- Less perceived risk within the business
Using AI to identify vulnerable customers enables contact centres not only to improve on consumer duty and meet the right ethical standards with empathetic and responsible service, it hugely decreases the risk of the worst possible outcome (from a business viability perspective) of an unexpected knock on the door from the regulator and/or widespread bad press.
To find out more about how CCP can help you make the right technology choices, read more here or get in touch.
This series of articles is drawn from our webinar with Jimmy Hosang, CEO and co-founder at Mojo CX. We explored seven key use cases for AI in contact centres, starting from the easiest productivity gains to value generating applications. You can find a summary of all seven use cases here, or watch the webinar in full here.
Moving up the value chain of AI use cases, consistent and effective agent coaching is a vital to the performance of contact centres. From areas that are critical to risk management, such as in regulatory compliance, or value-driving in improving customer experience and brand perception.
Traditionally, coaching relies on the same small samples and manual evaluations as QA (per use case 2), which inevitably means observations are sporadic and opportunities for improvement missed.
What is the AI doing in Auto Coaching?
Auto Coaching harnesses artificial intelligence to analyse agent interactions. It ‘listens’ to the conversation to identify areas of strength and opportunities for development. These data-driven insights then inform an AI-generated, individual agent coaching plan. Providing their coach with the tools to cater to individual agent needs and foster continuous improvement.
Key benefits: Efficiency
When you consider that 60-80% of a team leaders’ time is spent gathering information (Mojo time and motion studies) from the likes of Excel or Power BI to knit together a story of performance – to bring together call data, performance stats and behavioural insights into one place – and deliver coaching sessions, it’s easy to see the benefit of AI taking on this task.
Not just in efficiency, where it is possible to shift from a 1:12 or 1:15 manager to agent ratio to closer to 1:18 without losing effectiveness, but increasing team leader job satisfaction. Where they feel that more of the work they do is making a difference. As with previous use cases, how you take this efficiency benefit is a choice. Either in headcount reduction, or in delivering more coaching – which in turn drives customer experience improvement, or redeploying resources to more strategic tasks elsewhere.
Coaching quality and consistency
What’s more, each coaching conversation will itself improve in quality, because the feedback is based on and prioritised by a much greater data sample both for individual agents and the agent population as a whole. It also ensures agents receive consistency in their feedback, not just in one-to-one manager/agent relationships, but again all managers across the whole contact centre are delivering the same messages on the same coaching points to improve the quality of interactions overall. Which means opportunities are no longer missed, and the opportunity cost diminishes, while also improving customer experience.
An example of this, particularly when integrated with other speech analytics and the QA scorecard of use case 2, could be for offshore contact centres, where the agents speak the language of their customers, but colloquialisms, dialect, accent, vocabulary, fluency, speech pacing or cultural differences result in misunderstandings or frustrations.
Personalised rapid development
With AI in the mix, you no longer need to wait to deliver coaching on specific issues. Or hope that you’ve picked up the key ones from the samples you have when reviewing manually, because the AI is dedicated to finding them on a daily basis. Meaning coaching points for individual agents can also be delivered in real-time, or near-real time depending upon implementation.
The consequence of this targeted, personalised rapid development is that team leaders are able to have the right coaching conversation in the right moment – or even that the agent can ‘self-coach’. Coaching becomes both more efficient and more effective. Agents develop more rapidly, picking up development points as they occur, not days later when it’s easier to have forgotten it (or perpetuated bad habits) and in bite sized pieces, making the feedback more digestible and memorable. Their job satisfaction is improved though faster progression and the business wins through better customer service, better selling or more impactful risk management.
Automated role play
A further step in the development of this use case is the potential for AI to synthesise customer calls for training at varying levels of complexity. Either to pick up systemic issues within the whole operation, or to pick up specific agent needs on the job, or as part of the grad bay, which can then itself also be automated in the analysis and scoring of agent responses, per use case 2.
Here we see real driving both efficiency and effectiveness throughout the contact centre. And again, by providing agents with confidence in a safe environment, other KPIs such as attrition can be positively impacted.
Implementation Considerations
As with all other AI use cases, integrations and data privacy are key considerations. But in this case, it’s important to consider your accuracy thresholds for the AI, and how you will test for accuracy so that team leaders are confident in the AI’s ability to deliver. Furthermore, you will need to educate team leaders and agents on how to use AI-generated feedback. Always think ‘Human-in-the-loop’ (HITL) to ensure coaching is still accompanied by all of the empathy necessary to make it successful.
Measuring Success
For this use case, consider monitoring agent metrics such as first-contact resolution, number of coaching points and CSAT as a measure of coaching effectiveness on a one-to-one basis, measures of coaching preparation time or manager/agent ratios as measures of effectiveness. Then more broadly consider agent retention rates as a measure of higher satisfaction and reduced turnover.
In summary, the key benefits are:
• Significant reduction of the 60-80% of time leader spent preparing coaching
• Shift of manager/agent ratio from c. 1:12 to 1:18
• Higher job satisfaction and reduced attrition among agents
• Higher job satisfaction among team leaders
• Improved CSAT and brand perceptions as service improves across the board
As we move up the value-chain, the AI does get more difficult to implement. However the payoff also tends to get bigger too. Auto Coaching can be considered a strategic investment in agent development, to foster a culture of continuous improvement, that leads to enhanced performance and customer satisfaction.
To find out more about how CCP can help you make the right technology choices, read more here or get in touch.
This series of articles is drawn from our webinar with Jimmy Hosang, CEO and co-founder at Mojo CX. We explored seven key use cases for AI in contact centres, starting from the easiest productivity gains to value generating applications. You can find a summary of all seven use cases here, or watch the webinar in full here.
Quality assurance (QA) is a staple of every contact centre, more so where compliance and regulation demand it. Traditionally, manual QA reviews are concerned with the customer interaction itself, are labour-intensive and typically cover only 1-2% of calls.
While manual QA will pick up some training points, through a lack of comprehensive coverage, it often misses systemic issues that haven’t become immediately obvious elsewhere in the organisation but that could be found buried in call analysis.
What is the AI doing in Auto QA?
Auto QA uses artificial intelligence to automate the evaluation of both customer interactions through transcription (remember use case 1 – autowrap) and sentiment analysis, and what the agent did on systems.
Let’s examine the benefits.
Key benefits: Comprehensive coverage
With AI, it is possible to cover 100% of interactions; to fully assess agent performance consistently and at scale across all interactions and all areas of the QA scorecard, and send alerts straight to a team leader’s desktop.
Resource optimisation
With manual QA, you typically see around a 1:30 or 1:50 ratio of manual QA people to agents. But with Auto QA, you can expect around a 75% reduction in that overhead. Which is significant when working on fine margins, either in headcount reduction, or redirecting those resources to transformation or speech analysis tasks as opposed to data gathering.
Consistent evaluations
As with any human task, while we may believe all QA people are using their scorecard and delivering in the same way, even with calibration sessions and financial incentives, the chances of that being the case are slim; you may already know this from those calibration sessions. Indeed, the interpretation of the calibration itself may be flawed – for example, two different people may have very different takes on what constitutes empathy.
So while an AI scorecard evaluation of a voice interaction may, for example, only be 80% accurate to begin with, it is consistently 80% accurate, as opposed to the potential for human analysis to vary significantly and most likely sit at a lower accuracy figure of around 65%. Meaning more calls are scored at greater accuracy overall.
Real-time feedback
Finally, the benefits of real-time feedback while softer, are easy to understand. And completely measurable via the scorecard.
First, immediately picking up training points allows the agent to implement improvements on the very next interaction.
And second, for an agent taking hundreds of calls a day, picking up a training point even a few hours after the call occurred – especially if the interaction reason or resolution is atypical – makes it harder for the improvement points to stick, even with the benefit of the call to hand.
Implementation considerations
Aside from systems integrations, data privacy and compliance – and instead focusing more on the vagaries, of AI – accuracy (or lack of it) immediately translates through to an impact on human resources, where a less accurate AI could result in wasting resources on issues that aren’t issues.
Which is why it is always desirable to ensure there are humans in the loop (HITL), both in training, developing and refining the AI models, or in the process of checking its conclusions before delivering feedback.
With a combination of human review and machine learning improvements, the 80% accuracy figure can be improved to 85-90% accuracy in around four weeks, at which point you can consider pointing the human resources to different tasks. For systems interactions, including chat, you would expect greater accuracy from the AI from the outset, as it immediately has controlled data to assess.
If you can achieve 95-100% accuracy, per Mojo CX’s claims, then you can be confident human resources are targeted to where they are needed most. It may even be that you are willing to accept a lower rate of accuracy if the QA benefits outweigh the wastage. This is a decision unique to your business. And so as with use case 1, it’s important to understand the true baseline that the AI is improving upon.
Elsewhere, you may choose not to assess 100% of calls for processing and ESG reasons. These are all tolerances and optimisations that you can test and set to deliver against competing KPIs.
Measuring Auto QA success
For any AI implementation, it’s important to measure its success as this will build the case for future implementations. Whether that’s headcount, resource allocation QA KPIs or any of the many other contact centre KPIs.
In summary, the benefits are:
· 75% reduction in QA processing time
· 50-100 x increase in evaluated interactions
· 15-25% increase in evaluation accuracy and consistency
· Greater and faster improvement in agent performance and CSAT
While undoubtedly a little more complex to implement than use case 1, implementing Auto QA builds on those foundations by making use of call transcription and taking it to the next level.
To find out more about how CCP can help you make the right technology choices, read more here or get in touch.
This series of articles is drawn from our webinar with Jimmy Hosang, CEO and co-founder at Mojo CX. We explored seven key use cases for AI in contact centres, starting from the easiest productivity gains to value generating applications. You can find a summary of all seven use cases here, or watch the webinar in full here.
Summarising calls takes time – anywhere from 10-30% of the call. And agents are almost always under pressure to get the task completed in as little time as is humanly possible to meet AHT and wait targets. This often translates to errors or even missing data. Which not only makes it hard for future agents to follow the story, it can be a regulatory challenge too.
AI-driven autowrap and summarisation tools are helping to alleviate this burden by automating the process, allowing businesses to cut handling times and improve CRM accuracy. According to Jimmy, it’s one of the easiest applications of AI a contact centre can implement.
What is the AI doing in autowrap?
Autowrap and summarisation technology uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to transcribe customer calls in real time. As calls progress, key details such as issues raised, resolutions, and next steps are captured automatically. This eliminates the need for agents to manually document call details, both reducing errors and freeing up time for more customer-centric tasks.
Key Benefits: Time and Cost Savings
By reducing the time spent on manual transcription, businesses can lower wrap times by 50%, which translates to reducing handling times by 5-15%. For a contact centre with 200 agents, taking the mid-point of 10%, this could result in a reduction of up to 20 FTEs, and delivering a 2-3X ROI from day one.
How you take this benefit is then your choice:
a) A productivity gain, even through natural attrition
b) A service improvement by reducing wait times or improving service, with longer call times to allow for better first contact resolution
c) Reinvest in more value driving AI use cases to build maturity
Call Summary Accuracy
With manual transcription, there is always the risk of errors or omissions. AI-driven solutions eliminate these risks by automatically capturing the most relevant data from each conversation, improving both the consistency and quality of CRM records.
Increased accuracy has a number of benefits, whether you run a regulated business or not. First is in future contacts, whether you met a first contact resolution goal or not. Any future calls where a customer refers to a previous call – and reasonably expects there to be some level of ‘corporate memory’ – can be shortened by avoid any lengthy re-explanations of what has gone before. Not only does this provide a future productivity gain, it makes for a far better customer experience too. So even at use case 1, we are already facilitating value generation through slick customer processes that avoid typical customer frustrations, as well as productivity.
What’s more, the data is clean, reliable and available for future analysis and QA. Look out for an article on use case 2, Auto QA, for more on that subject.
When building a business case, these are important considerations; it’s important to remember that your baseline probably isn’t perfection. And so your quality uplift may be greater than you have otherwise anticipated.
Easy Integration: No Overhaul Required
While it is undeniably desirable to integrate Autowrap technology into CRM or policy admin systems, it’s not a pre-requisite to start making these gains. An agent – dubbed the ultimate API in our recent whitepaper– can easily check through the summary, make any necessary amendments if you require it (your benchmark of what is good enough will depend on your business) and copy and paste it in. They’re already used to connecting disparate systems and will be working where you want to capture it anyway.
This means that businesses can buck the trend of AI project failure and quickly adopt the technology with minimal disruption to existing workflows. Once the ‘short, sharp’ solution is working, of course you can consider and implement the deep integrations to automate the task, but you will be most of the way there without it.
Enhancing Agent Experience and Customer Outcomes
As alluded to earlier, the benefits aren’t just about reducing operational costs—they also enhance both the agent and customer experience. By automating mundane, and often poorly executed tasks like call transcription, agents are free to focus on more valuable work, such as problem-solving and building customer relationships.
This not only boosts job satisfaction – which in itself may then also translate to tenure, sickness and recruitment gains – it also contributes to higher-quality customer interactions. Look out for use case 5, ‘Agent Assist’ for more on this topic.
Measuring Success
For any AI implementation, it’s important to measure its success as this will build the case for future implementations. Whether that’s headcount, resource allocation or the gamut of other contact centre KPIs.
In summary, the benefits are:
1. Immediate productivity gains of c. 10% of agent all handling time
2. Improved accuracy of note taking
3. Customer satisfaction gains from better corporate memory and more attentive agents
4. More time available for valuable conversations
5. Employee satisfaction gains – happier agents, longer tenures, less sickness, reduced recruitment
6. Regulatory compliance improvements
7. Easy and scalable implementation to shorten implementation timescales and increase AI success
8. Ability to re-invest gains in building AI maturity
Ultimately, accurate (enough) autowrap is an obvious win in any contact centre.
To find out more about how CCP can help you make the right technology choices, read more here or get in touch.
This series of articles is drawn from our webinar with Jimmy Hosang, CEO and co-founder at Mojo CX. We explored seven key use cases for AI in contact centres, starting from the easiest productivity gains to value generating applications. You can find a summary of all seven use cases here, or watch the webinar in full here.
AI in the contact centre is no longer a question of if, but where to begin. In our recent webinar with Jimmy Hosang, CEO and Co-founder of Mojo CX, we explored seven practical, high-impact AI use cases that are already delivering returns in real-world operations. From automating wrap-up notes to exploring full voice AI, the conversation cut through the hype to focus on what’s truly working – and what’s coming next.
From productivity savings – and easy wins – to value generation, here we summarise each of the seven use cases, their benefits, pitfalls, and what it takes to make them work.
1. Autowrap / Call Summarisation
This is one of the most immediate and measurable wins for AI – and it’s relevant to every contact centre, whether procedural or regulatory. With AI transcribing and summarising calls, wrap time is reduced by 50% and average handling times by 5–15%. In a 200-seat contact centre, at 10%, that’s equivalent to freeing up 20 full-time agents.
It’s an easy sell for operations leaders: the 2-3X ROI is immediate, the data is clean (and doesn’t need complex integrations, a simple copy/paste will do to start), and the impact on agent workload is obvious. What you do with the benefit is up to you; save the 20 FTE through natural attrition, reduce wait times, improve service. Less typing, less admin, more time for real conversations.
2. Auto QA (Quality Assurance)
Manual QA processes typically only cover 1-2% of calls. With AI-powered auto QA, every conversation can be transcribed and assessed, increasing both coverage and scorecard accuracy, with the potential to reduce QA overhead by 75%. Once the model reaches high accuracy (which can be achieved in four weeks or less), it enables a rethinking of QA resourcing. Where teams can reinvest those hours into value-adding activities like deep-dive analysis or real-time speech insights.
What’s more evaluation consistency is likely to see an immediate uplift, as is agent performance through real time feedback.
3. Auto Coaching
Team leaders spend 60-80% of their buried in fragmented data or playing detective to understand performance issues. Auto coaching can bring together call data, performance stats, and behavioural insights into one view – streamlining prep time and allowing leaders to focus on actual coaching.
From an efficiency perspective, this facilitates a shift in manager-to-agent ratios from 1:12 or 1:15 to something closer to 1:18 without losing effectiveness. But beyond that, coaching quality and consistency improve and agent development is more pointed and expedited. It also unlocks the potential for automated role play both on the job and in grad bays. This provides the basis then for both greater job satisfaction among both managers and agents, as well as delivering higher quality interactions throughout the operation. All of which have an impact on broader measures such as agent attrition, CSAT and brand perception.
SIDE NOTE: While those first three use cases focus a lot on the potential for reduction in headcount, it’s often more about doing better work, not just less work. Think: HITL (Human in the Loop), not human out of the picture.
4. Identifying Vulnerable Customers
This is where AI starts playing a key role in risk management and regulatory compliance. Agents can’t always be relied upon to spot vulnerability signals in real time – especially when they’re under pressure to do many things at one in a short space of time. AI can listen in and flag when it detects signs of vulnerability, alerting the agent in the moment and ensuring the right customer journey is followed.
The benefit? Reduced regulatory risk, better outcomes for vulnerable customers, and more confidence in compliance reporting. This use case also pairs naturally with summarisation – capturing the right context and actions in the CRM.
5. Agent Assist
Beyond risk management and efficiency, AI also enables agents to add value in the moment. Agent Assist tools analyse the live conversation and suggest actions – whether it’s handling a low-value enquiry quickly, spotting a sales opportunity, or guiding a customer toward a better outcome.
This is where things get exciting. AI is no longer just reducing cost – it’s helping unlock customer lifetime value and improving journeys. It’s also a mindset shift: from cost centre to value driver.
SIDE NOTE: The constant push for self-serve may well be eroding brand loyalty, where a great conversation with an agent isn’t only about making a sale or solving a query, it’s an experience that plays into customer brand perception.
6. Hands-Free Conversations
Imagine an agent who doesn’t have to type, click around systems, or juggle tabs – just talk and listen. That’s the promise of hands-free conversations. With AI handling navigation, form filling, and admin tasks, agents can give customers their full attention.
It’s not just about productivity, it’s about truly human interactions that focus solely on the customer. How satisfying would that be? It could change the type of people you hire and shift expectations around what great service looks like.
7. Full Voice AI
Everyone’s chasing the holy grail: fully autonomous AI voice agents. Why? 24/7 customer contact, instant routing, and scalable service without scaling headcount.
But Jimmy’s message was clear – don’t rush it, though do keep your eyes on the prize. Build your maturity and path to value with easier use cases, underpinned by the right data and processes. This isn’t about flipping a switch – it’s about a journey to transformation.
Final Thoughts: Think “value first, tech second”
Across every use case, the AI you deploy is about outcomes. Whether that’s saving time and cost savings, improving job satisfaction or deepening customer relationships, AI only succeeds when it’s introduced with purpose.
Start small. Pick the use case with the clearest ROI. And don’t be afraid to move fast – but move smart.
In today’s outsourcing landscape, success depends on much more than cost savings and process efficiency.
On 25th February 2025, Neville Doughty and Phil Kitchen from the Customer Contact Panel hosted a webinar with Joe Hill-Wilson, CEO and Co-Founder of Learn Amp and Martin Hill-Wilson, Owner of Brainfood Consulting, to discuss Sustainable Operating Models in Outsourcing. One of the most important takeaways from the discussion on sustainable operating models is that Learning and Development (L&D) must be embedded into the core of every outsourcing strategy. Without continuous learning, sustainability simply isn’t possible.
Why Learning and Development is a Sustainability Driver
In outsourcing environments, teams often face rapid change, evolving client expectations, and shifting technologies. This is reflected in the data – 92% of organisations are facing high or very high risk of top talent leaving in the next year (Brandon Hall Group, HCM Outlook, 2024). Without a structured and ongoing approach to skills development, outsourced teams can struggle to keep pace, leading to inconsistent quality, reduced productivity, and higher turnover . During the webinar, 82% of attendees reported that current procurement practice restricts the value they can bring to their clients.
The key takeaway? Organisations that embed L&D into their operating models create more resilient, adaptable, and future-ready outsourcing workforces.
Challenges in Sustainable Learning for Outsourced Teams
The panel discussed the various challenges companies face when it comes to embedding learning into outsourced operations:
- Geographical and Cultural Gaps: How can we create a unified learning experience for teams spread across different countries, cultures, and time zones?
- Engagement and Adoption: With high attrition rates common in outsourced environments, how do we motivate teams to actively engage in learning?
- Measuring Impact: How can we quantify the ROI of learning programs in outsourcing partnerships?
What Effective L&D Looks Like in Sustainable Outsourcing
When looking at solutions for the challenges discussed, the panel noted the importance of centralised learning platforms that deliver consistent, engaging content to all locations. Platforms like Learn Amp help organisations create:
- Standardised onboarding programs to accelerate time-to-competence.
- Bite-sized, mobile-friendly learning content to fit learning into busy shifts.
- Social learning spaces that encourage peer-to-peer knowledge sharing.
- Data dashboards to measure engagement, skills development, and business impact.
Embedding L&D into Operating Models: 3 Key Strategies
Treat L&D as a Business Process, not a Project
Learning shouldn’t be an afterthought or an annual event. It needs to be a continuous, embedded process that evolves with the business and its outsourcing needs.
Make Learning a Shared Responsibility
Learning success shouldn’t fall solely on HR or L&D teams. Operations managers, team leaders, and employees themselves all need to co-own learning outcomes.
Measure What Matters
Sustainable learning models measure not just completion rates, but real business impact: faster onboarding; fewer errors; higher customer satisfaction; and improved employee retention. The LinkedIn Workplace Report shared that 94% of employees would stay longer if companies invested in their development.
Key Takeaway
If there’s one key takeaway from the webinar, it’s this: sustainable outsourcing depends on sustainable learning. When organisations invest in embedding learning into every stage of the outsourcing lifecycle, they create an employee experience where team members thrive.
If you would like to access a copy of the recording it is available here: Webinar Link
The year ahead promises to be a turning point for customer contact. AI and automation are advancing at an unprecedented pace, yet businesses are facing economic uncertainty, rising costs, and rapidly shifting customer expectations. The pressure to adopt new technology and improve service levels means leaders must make bold, strategic choices.
At the end of 2024, we held our annual ‘Big Conversation’ to uncover key challenges for the year ahead and hear directly from cross-sector contact centre leaders about how they’re addressing them. These insights have shaped our latest whitepaper, 2025: A Year of Difficult Conversations?. In this paper, we explore those challenges in detail and outline priorities and solutions. One theme dominates: success in 2025 will depend on how well businesses navigate ‘difficult conversations’—both within their organisations and with their customer and suppliers.
How can you make the right tech decisions in the age of AI?
AI can be a powerful tool for improving operational efficiency. However, the reality is stark: according to Gartner, 80% of AI projects fail, which is twice the failure rate of non-AI projects. Despite this, the pressure in the boardroom to “do something with AI” is stronger than ever. The key question isn’t whether to implement AI, but how to do so strategically and safely.
When AI is implemented well it can deliver valuable results. But the risks of adopting this still fledgling technology can be significant—wasted investment, damage to reputation, and disruption to operations. The businesses that succeed with AI will be those that clearly define its use cases, align them with business goals, invest in high-quality, integrated data, and ensure that AI complements human expertise rather than replacing it. AI has the potential to be a game-changer—but only with careful consideration.
How do we meet economic, regulatory and resource challenges?
While grappling technology decisions, contact centres also face ongoing economic headwinds, regulatory challenges and a 15% decrease in headcount since 2019.
As businesses introduce new contact channels and explore innovative solutions, the fundamental customer need remains unchanged—a fast and effective response
But despite the rise in self-serve and co-pilot automation, customer satisfaction in the UK has declined. While automation is handling simple queries, agents are left to tackle only the most complex cases with fewer resources overall. Agents have little respite from more intense interactions and operations have fewer agents available. Even with future AI implementations, research predicts relatively modest headcount reductions of a maximum of 15%.
What’s more, in 2025, UK contact centres will need to absorb and manage an 8-10% increase in agent costs. Meanwhile the ongoing cost of living crisis means customers remain stressed and regulatory requirements add to operational demands —all against the backdrop of a muted growth forecast and ongoing economic challenges. No wonder things feel pressured.
Consequently, leaders are exploring various ways to optimise their service models, including offshoring, automation, or refining their approach.
Getting It Right: From Good to Great
One thing is clear. Transformation isn’t optional—it’s essential. The businesses that thrive in 2025 will be the ones that take a proactive approach. The most successful organisations will define clear, achievable AI use cases, align data, technology, and human expertise, prioritise governance, security, and compliance, and engage employees in AI adoption from the start.
The path ahead will present both opportunities and challenges, but with the right strategy, tackling today’s difficult conversations can pave the way for a stronger competitive edge tomorrow.
Read our paper for more detailed analysis of the challenges, but more importantly, how to tackle those challenges and put in place a positive programme of change.
The Whitepaper is free to download and immediately accessible below. We would love to hear your experiences too. Follow us on LinkedIn to share your thoughts.
In early February I attended the IP Integration “Spotlight” event at the Midland Hotel in Manchester where we were provided access to some great insights from the team and from Steve Morrell of ContactBabel, what follows are my thoughts and reflections arising:
Something around customer adoption of automated solutions has been playing on my mind, it often happens when I suggest someone talk to an automated bot solution so they can experience first-hand how far the technology has come, where it is going and what the real possibilities are.
Being in the CX world and having several partners on our network that have such solutions, I have a number saved to my phone, just for this type of conversation. If I pull the phone from my pocket, find the number, dial it and hand it someone to have a conversation then I often feel that the “conversation” isn’t as free flowing as it should be. Why? Well that is a great question.
I suppose it could be that for the past 15 years when contact centres have effectively forced customers to speak to automated voice response systems, we have typically limited customer so saying one word “listen to the following list of options and then say the option you would like” or “in a few words please say why you are calling today” so for years we’ve been saying ‘please speak to this automated system in a short staccato format’. Now, in a matter of a couple of years, some businesses are offering customers the opportunity to speak freely to their bots or automations, whilst others are still on the limited few words space. No wonder consumers get confused – and the acceptance and adoption of voice automation could well be held back as a result.
Voice is here to stay?
The truth is that voice interactions are still our favoured route of contact as customers, when it comes to getting things done and obtaining reassurance that we’ve been heard. Whilst the death of voice in contact centres has been forecast for the past 20 years, the reality remains that voice is here to stay, millennia of evolution cannot be undone so quickly. Data shared at our webinar on the State of the Customer Experience Market with David Rickard of Everest Group in November (article link) validated this, as their research highlighted that 72% of revenues amongst the outsource community were still coming from voice-based activity in 2023 when both agent supported voice and conversational AI driven interactions were considered.
The data shared in the room in Manchester by Steve Morrell of ContactBabel corroborated this view, with 64% of interactions being cited as voice in his forthcoming 2025 report. Also that we are so keen to ensure that we speak to someone that we will now wait in the longer queues that have been identified post pandemic and that we have accepted these as the norm.
So, as a human race we have a deep attachment to use of voice, however I’m still receiving articles daily which suggest otherwise – and ours is an industry which is based on employing people to talk to customers. We need to acknowledge that ‘the bots’ or automation is coming for our lunch, which according to an article in the New York Times on February 1st it may however already be in a place to arrange someone to bring our lunch and where may that end?
An article by Kevin Roose details several tasks which he managed to complete using OpenAI’s Operator, a new AI agent in the week prior. Most of the tasks it did autonomously with minimal intervention. It met its brief of being an AI agent that uses the computer to accomplish valuable real-world tasks, without the need for supervision, to complete tasks in the background with a handoff back to the user to enter passwords or payment card details. However, in Kevin’s article he talks of how it ordered lunch to be delivered to a colleague’s house and responded to LinkedIn messages well, up to the point where it started signing him up to attend webinars, amongst other tasks. There were, however, several tasks where the automation struggled or needed an amount of reassurance or confirmations. Because of which he felt that it would have been faster to do the tasks himself, but acknowledged that the AI agent is at an early stage of development.
What we do know is that the evolution of technology is only gaining pace. Peter Diamandis, founder of the XPRIZE (https://www.xprize.org/) , is cited as having said in 2020 that “the next 10 years will bring more progress than the last 100 years” Given the pace of change in the past 5 years, it is reasonable to assume that Moore’s Law will hold true in this instance – and that we need to be ready for this.
As humans we like voice, we choose voice. But if personal assistants in the form of OpenAI’s Operator or DeepSeek were to be adopted by the general public (your customers) to complete their home admin tasks, then these systems won’t have the same emotional connection to voice conversations and will be happy to interact directly with a company bot. However, how quickly will we reach that point?
Public adoption is key then?
We can implement the best solutions in the world, but if nobody uses them, what use are they?
Whatever is coming next, we have a dependency on customers to embrace and use those solutions, whether that is voice automation in the contact centre or the potential for the eventual use of “their own” automation by customers to engage with brands to resolve issues.
We’ve seen before conversations around ‘brand by-pass’. Now, using an Alexa or alternative voice-activated AI assistant to complete simple tasks is clearly the gateway to us getting to a point of asking technology to, say, engage with our utility provider to amend our direct debit or to find a cheaper insurance renewal. At this point we as individuals will have less input to what brands we choose to purchase, so then the brands that will succeed are those that are easiest for our automations to interact with.
But before we get to this utopian vision of admin free lives with our AI assistants ensuring the effective running of our homes and lives, we need to pass a point of public adoption of AI.
A 2023 report from Ipsos shows that 66% of people they surveyed globally expect that products and services using artificial intelligence will profoundly change their daily life in the next 3-5 years. Whilst this is the average, the range of responses on a country and demographic level vary considerably, with the proportion expressing this belief in South Korea as high as 82%, whilst France sees the lowest number agreeing with this sentiment at 51% (we in the UK see 58% agreeing with this statement).
Products and services using artificial intelligence will profoundly change my daily life in the next 3-5 years – 66%
So, whilst there is broad agreement that services using artificial intelligence will change our lives, what people are willing to adopt and how is a key consideration, acknowledging that some will be unable to adopt due to a variety of reasons.
The conversation at the Spotlight event therefore quite naturally centred on work that could be done to implement changes or applications of AI to better support the contact centre agents in delivering service efficiently without too much impact to the customer, generating a series of marginal gains which support the agent in resolving customer queries, potentially reducing call durations and in turn queues and repeat contacts – a series of win/win scenarios which:
- Improve service
- Reduce pressure on the contact centre team
- Reduce repeat contacts
- Reduce the time customers spend trying to get through
- Reduce costs
- Improve staff wellbeing
Changes which fulfil the appetite of businesses to implement changes and leverage AI, but consider how willing customers are to adopt these changes.
Is some re-programming required?
If we want the possible AI solutions to be successful, we will have to consider how we guide customers to use these solutions most effectively. Our industry has created a sub-optimal situation through a combination of poor customer experiences in the past, limited system capabilities and a “tell me in three words” approach. If we want customers to embrace the possibilities of technology, then we need to bring them on the journey.
Consider how self-serve check-outs have become the norm when we are out shopping in recent years . There is a journey that I’ve certainly been on to this point, which I discussed with IPI’s Sam Grant at lunch.
Coming prepared, we need our customers to come to the contact prepared to engage with AI.
Similarly, from prior experiences I soon learned that I need to stop putting my shopping bag in the bottom of my basket, then putting my items of purchase on top of it, which created friction in the process when I needed to get to my bag to enable me to pack items as I scanned them. So, ideally, we need our customers to come to the contact prepared to engage with AI (unless they don’t want to?)
Offering a choice? Do I want to self-serve or would I prefer to queue?
When I’m approaching the tills, I can see a queue for a till with a cashier or I can see available self-serve checkouts. If I can also see someone there by the self-serve tills to support me, then I can make an informed decision.
Unexpected item in bagging area! Solutions need to be flexible enough to minimise friction.
That bag I just dug out from my basket, I’ve tapped that I’ve brought my own bag, but it is perhaps heavier than the scales expect, therefore I’ve got an unexpected item. I’m removing and resetting the bag but there is a red flashing light and now I’m waiting for someone to come help me. We’ve all been there (please tell me this wasn’t just me!). The solution has now evolved, though, replacing scales either with additional trust by the retailer, or with cameras, but the result is a smoother customer experience.
Authorisation for purchase There will be times when someone must step in. If so, ensure it is done in a timely fashion.
OK I bought wine, it’s the weekend, please don’t judge me. The process to verify that I’m of age and can make that purchase has parallels also. We need to ensure that if a customer needs support then it is quickly available. Now I want those annoying flashing lights to flash brighter, because I need help to complete my purchase.
How do you want to pay? Payments need to be frictionless, tap and go, no creased banknotes!
The same will apply to your callers they need to be able to make the payment without being moved to another channel and of course you need to ensure you are properly protecting that payment data.
Do you require a receipt? perhaps we need to acknowledge that customers will want validation of their conversation, of what was committed to and that they can trust that it will be done.
It has taken me a long time to reach the point of clicking no to a paper receipt. I want to be able to evidence that I’ve paid and not just walked round the shop popping things in my bag. Part of the reason so many of us are still reverting to speaking to a human when we have an issue, other than our lived experiences of trying to explain a complex situation in 3-word blocks, has to be that we can say “I talked to …. And he said he’d sorted it”.
What does it all mean?
People are complex. The implementation of self service and automation of the simpler query types means that average contact centre conversations are now much longer than they were and with rising staff costs there is a clear pressure on businesses to make changes to reduce customer servicing costs.
There is a broad spectrum of solutions available to support businesses address these challenges, whether outsource or technology. These need to be properly aligned to your objectives, and it is likely that you may need to speak with someone around how to select, prioritise and deploy these solutions.
If you need to chat then feel free to drop us a line.
Collectively Customer Contact Panel (CCP) have a lot of experience in contact centres and CX. However, as things are changing rapidly in the world of AI, we met with CCP to discuss some of the broader considerations, including what technology we could deliver as an alternative view of what could be our probable future reality with the support of AI – we agreed we would share the output.
The art of the possible?
We can talk about the pace and the tone of this piece, however the reality is that with appropriate questions raised and some boundaries that we included (some for our amusement) the content within this 10 minute AI generated “BotCast” not only demonstrates the capabilities of AI, but raises some interesting questions and considerations as to how CX evolves and what guard rails need to be in place.
Click here and have a listen, and of course, if you want to discuss we’d be happy to deploy some of our humans.
When you assemble a room of people with extensive levels of contact centre experience, as we did for our event hosted at Sutherland Labs, you know from the noise levels over coffee there are going to be some great conversations! Add some fantastic speakers from our outsource and technology networks to share their views of the market and a lively, open dialogue around challenges and opportunities (new and old) will follow.
We are looking forward to continuing these conversations and scheduling another event. But in the meantime, how do we bring so much collective experience together in a short article that does justice to the quality of the conversations?
Navigating Business Decisions in a Rapidly Evolving Landscape
In the current environment, companies face a range of critical decisions, from implementing new technologies to fostering employee engagement. Despite knowing what needs to be done, many organisations struggle to translate that knowledge into actionable outcomes. This disconnect is often a result of inadequate systems, outdated training and coaching models, and an inability to adapt to change.
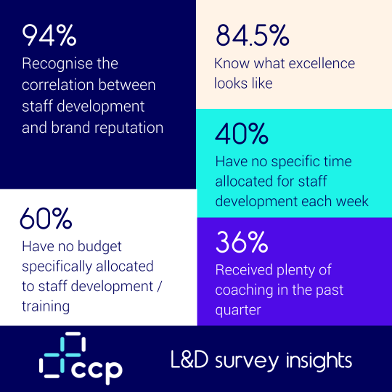
In our recent L&D survey it was apparent that there is a clear gap between knowing and doing. Results show that while employees understand their roles, there’s a significant disconnect between knowledge and execution. This is particularly evident in how businesses approach training, often relying on outdated, “once-and-done” programmes that fail to evolve alongside the changing work environment. As companies shift to remote work, many are noticing a reduction in employee loyalty and engagement, partially because of the lack of in-person interaction and relationship-building.
Addressing the Changing Needs: Evolving Training and Technology
To bridge this gap, organisations must rethink how they train their employees, particularly if they are to continue with a work from home or hybrid working model. Has enough been done to redesign training and refresher modules that better fit a virtual environment? Equally, more needs to be done to focus on continuous education rather than static, one-time courses which tick a box for compliance. Furthermore, conversational AI can be a powerful tool in reshaping learning; allowing employees to ask dynamic, evolving questions rather than relying on predefined solutions.
“Businesses recognise the correlation between staff development and brand reputation, but may not always apply the budget to ensure delivery”
AI offers the potential to unlock the true capabilities of people and data, but as we have said before is not a silver bullet. It can revolutionise business processes by supporting employees in their roles, reducing friction, and enhancing decision-making. AI can also help agents manage customer queries more efficiently, giving them access to foundational knowledge in real-time. However, the challenge lies in positioning AI correctly: not as a threat to jobs, but as a tool for augmenting human capabilities.
For example, AI’s ability to analyse customer intent and apply insights to guide agents through complex interactions can dramatically improve customer experience (CX). By properly integrating AI into business workflows, companies could potentially resolve the eternal challenge of moving from being seen as a cost centre to profit centre, unlocking new value opportunities across the customer journey.
Location strategy is still a consideration as the global market evolves. The outsourcing industry, particularly in sectors like fintech, IT support, and healthcare, appears poised for significant growth. We know countries such as South Africa have already emerged as strategic hubs for business services, offering talent and capabilities that align with the growing demand for multilingual and technologically adept service providers. Whilst there are valid concerns as to the capacity that remains available, with 33% unemployment in South Africa (60% for young people) as well as the wider continent opening for business, then combined with the capabilities of technology great opportunities remain available.
Overcoming Challenges in AI Adoption
While AI presents numerous opportunities, it also comes with significant challenges. Many process owners may be hesitant to adopt AI due to concerns about how it will impact their workforce and customer relationships. Meanwhile, senior leadership may be focused more heavily on the potential cost saving benefits. There’s a widespread misconception that AI will replace jobs, particularly in customer service. However, AI’s true value lies in assisting and enhancing human roles, not replacing them.
For businesses to adopt AI successfully, they need to:
- Align AI with company goals and culture: AI should be seen not as a technology investment, but as a strategic asset that drives both customer and employee experience.
- Shift from a cost-saving mindset to a value-driven approach: Technology shouldn’t be about cutting costs; it should unlock value, address problems at their root cause and improve service quality.
- Build the right business case: Secure buy-in from different budget owners by emphasising how AI can enhance outcomes across the organisation.
Aligning Metrics and Culture for the AI-Driven World
To fully leverage AI’s potential, cultural and operational changes are required. Business leaders need to:
- Align metrics with an automated world: Ensure that technology handles routine tasks, allowing people to focus on complex, human-centric work.
- Redefine the agent role: The agents of the future will need to deliver more value and possess different skills compared to traditional customer service roles.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement: Embrace ongoing evolution, where AI serves to complement human skills and free up time for higher-value tasks.
- Focus on proactive engagement: Let technology handle the repetitive, allowing people to engage with customers in a more meaningful way.
- Encourage bravery in decision-making: Leaders must support bold decisions around AI investment to drive long-term success.
Rob Wiles, Zoom“AI is not the solution, it is a key to unlocking it”
Irrespective of delivery location, the future of CX delivery will increasingly rely on AI and automation to enhance customer journeys, optimise operations, and drive sustainable growth.
Transformation is never-ending. Businesses must approach AI and automation not as one-time projects but as ongoing evolutions. This requires understanding the unique challenges they face, aligning technology with business goals, and ensuring that AI enhances rather than replaces the human element.
With the right strategy, AI can unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth, helping companies stay competitive in a rapidly changing world. However, without the appropriate attention to employee experience, success will be illusory or limited.
Delivering the right experiences
At Customer Contact Panel we support organisations in delivering contact centres that match their ambitions. In a Deloitte Digital research articles from May 2024 it was cited that 55% of contact centre leaders reported that they didn’t meet their strategic goals in 2023 and 76% reported that their agents were overwhelmed by systems and information*.
If you are facing challenges meeting your strategic goals or fulfilling the ambitions you have for your people, customers or technology, we have the experience to support you. Just ask.